Walls serve as structural partitions and environmental barriers in buildings. They may be load-bearing or non-load-bearing and are typically composed of materials chosen for their strength, insulation properties, and compatibility with finish systems. In most modern construction, plastic-based products are used extensively in the insulation, flashing, adhesives, sealants, and surface treatments, making them a central point of concern for zero-plastic building strategies.
Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs)
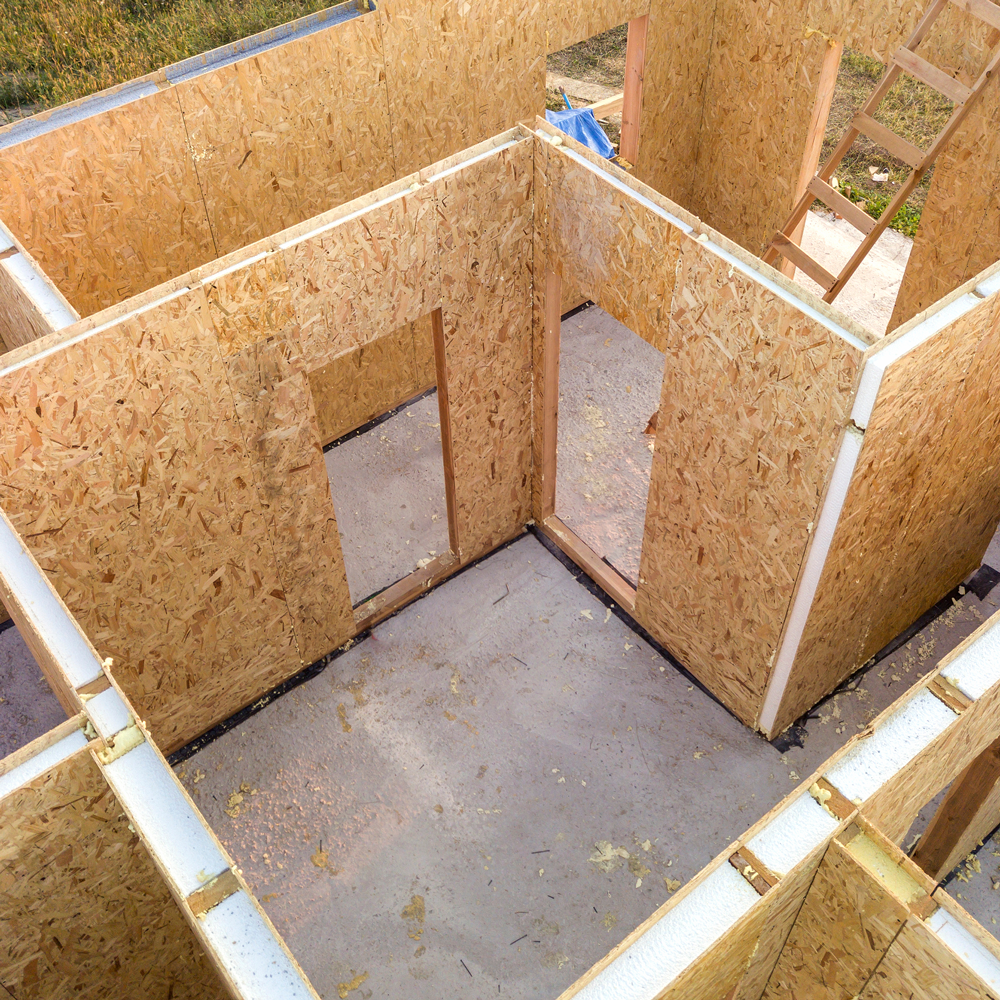

SIP walls on a construction site
SIPs are prefabricated panels composed of a rigid foam insulation core (often expanded polystyrene or polyurethane) sandwiched between structural facings, typically oriented strand board (OSB). The foam core, the engineered wood sheets, and the adhesives used in assembly are all plastic-based. While it could be theoretically feasible to use non-engineered wood, mineral wool insulation, and fasteners in place of adhesives to create a product with similar form & function, no commercial SIP systems are currently available without plastic materials.
Insulated Concrete Forms (ICFs)
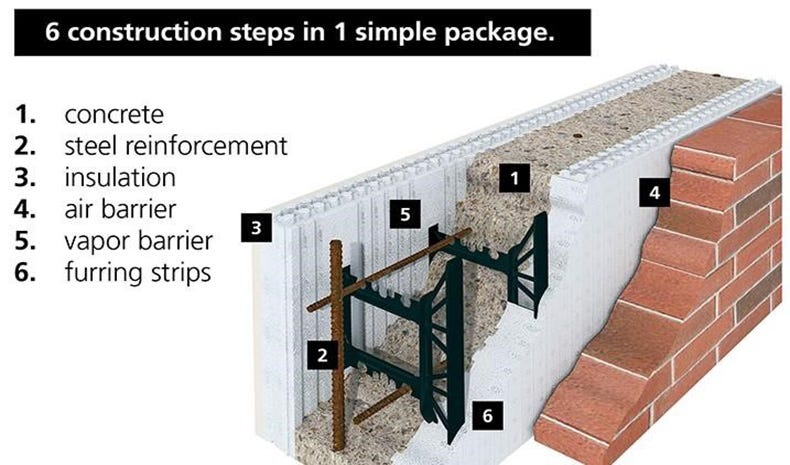
Diagram of ICF wall composition
ICFs consist of interlocking plastic foam blocks (usually expanded polystyrene) into which concrete is poured. The foam remains in place to serve as insulation. Additional plastic components such as vapor barriers and furring strips are often integrated. Alternative insulation strategies for concrete forms are largely undeveloped, and current ICF systems rely almost entirely on plastics.
Drywall

Tradesmen hanging drywall on a construction site
Drywall is composed of a gypsum core faced with paper. In modern manufacturing, various plastic-based [1] process additives are used: dispersants, accelerators, retarders, fiberglass reinforcements, and hydrophobic agents like silicones or waxes. [2] Although these chemicals make up a small percentage of the total product by volume or mass, they are difficult to avoid in current supply chains. Available publications are unclear on whether drywall itself contains small quantities of residual polymer; this will require physical testing of available products.
Concrete walls
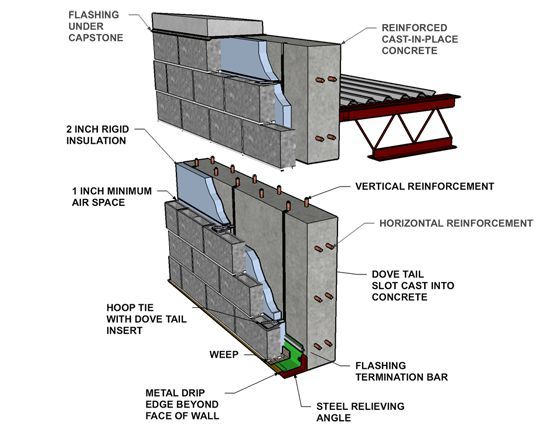
Concrete wall system diagram
Site-cast concrete walls, excluding those using polymer-modified concrete or plastic reinforcement, can be constructed without plastic. Traditional steel rebar, careful joint detailing, and mineral-based finishes allow for fully mineral-based wall assemblies.
Masonry walls
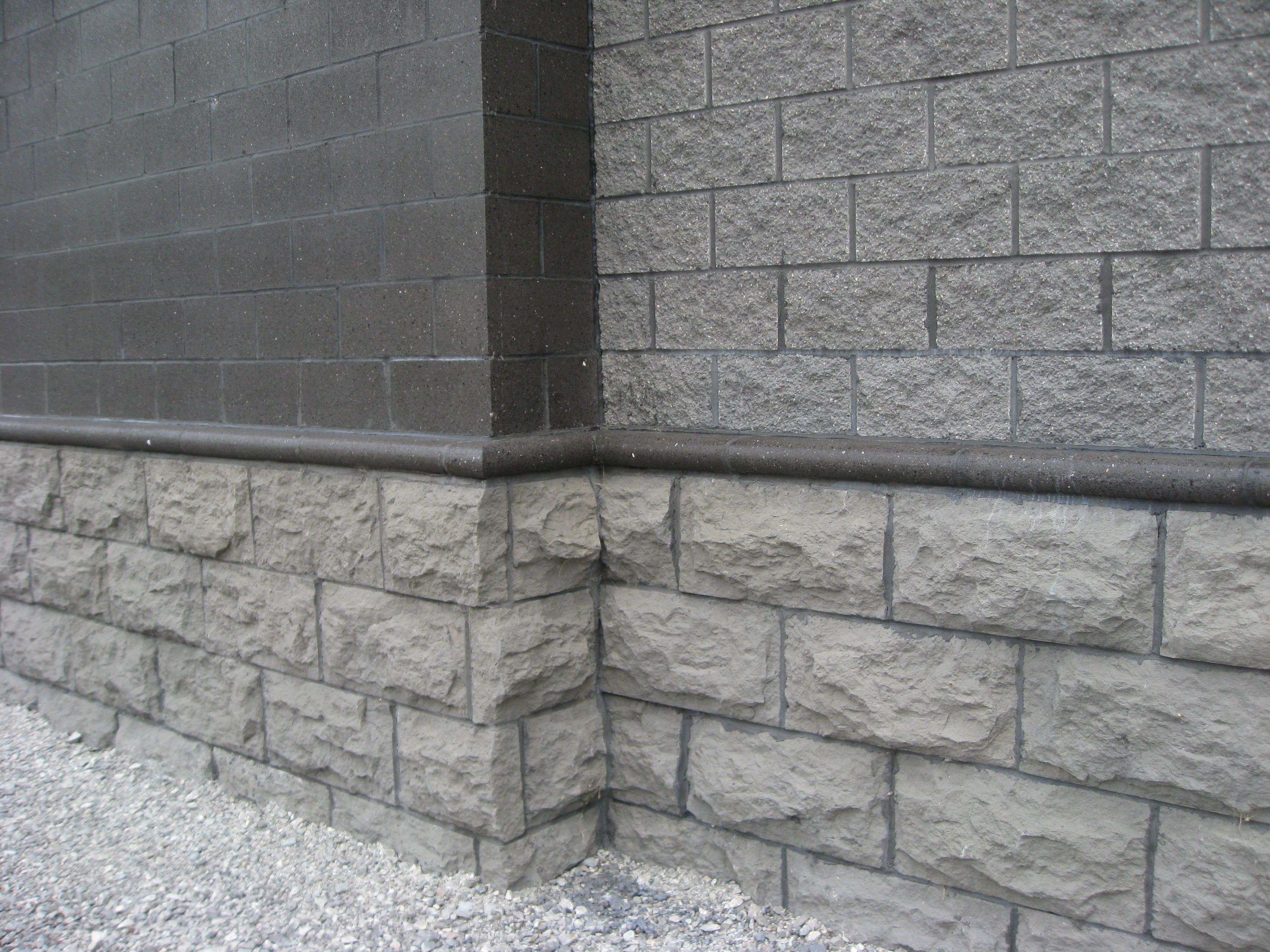

Masonry walls
Masonry construction includes clay bricks, terracotta, stone, concrete blocks, and other mineral units joined by mortar. Provided that grout and mortar mixes do not contain synthetic admixtures such as plasticizers or shrinkage reducers, these walls can be built without plastic. However, modern masonry assemblies often include internal or external insulation, vapor barriers, or synthetic flashing, all of which introduce plastic. Historic flashing techniques using sheet metal or mortar shaping are suitable alternatives.
Plaster
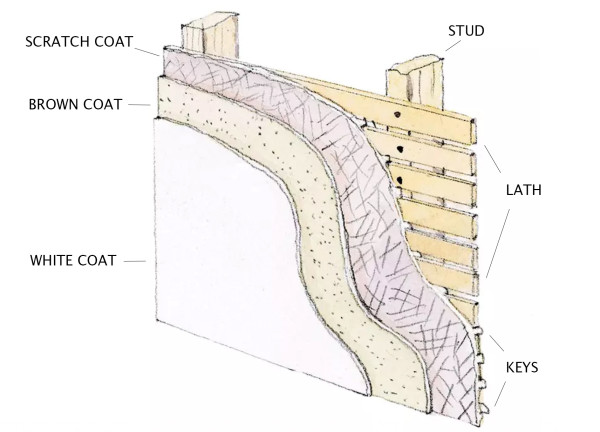
Diagram of lath & plaster wall system
Interior plaster walls are typically applied over wooden lath. Standard plaster is lime- or gypsum-based and free of plastic. However, fire-retardant variants may contain additives such as polystyrene beads. Wood lath systems are sometimes made with engineered woods.
Metal wall panels
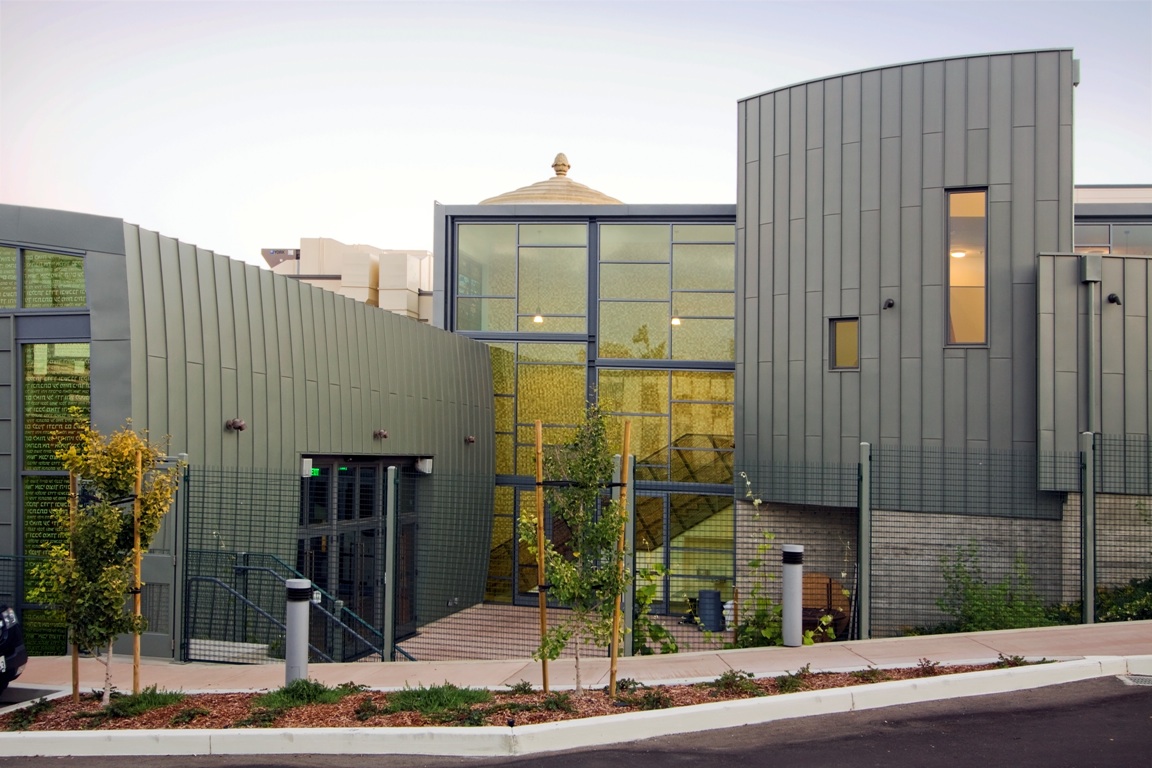

Single-skin metal panel cladding
Single-skin metal panels, which are typically cold-rolled or pressed into profiles and mounted directly to wall framing, can be plastic-free if unpainted or coated only with traditional finishes like oils, oxides, or electroplating. However, most modern metal wall systems, including insulated metal panels (IMPs) and metal composite materials (MCMs), incorporate rigid foam cores or polyethylene layers. Powder-coated or resin-coated surfaces also introduce plastics.
Plastic-related components in wall systems
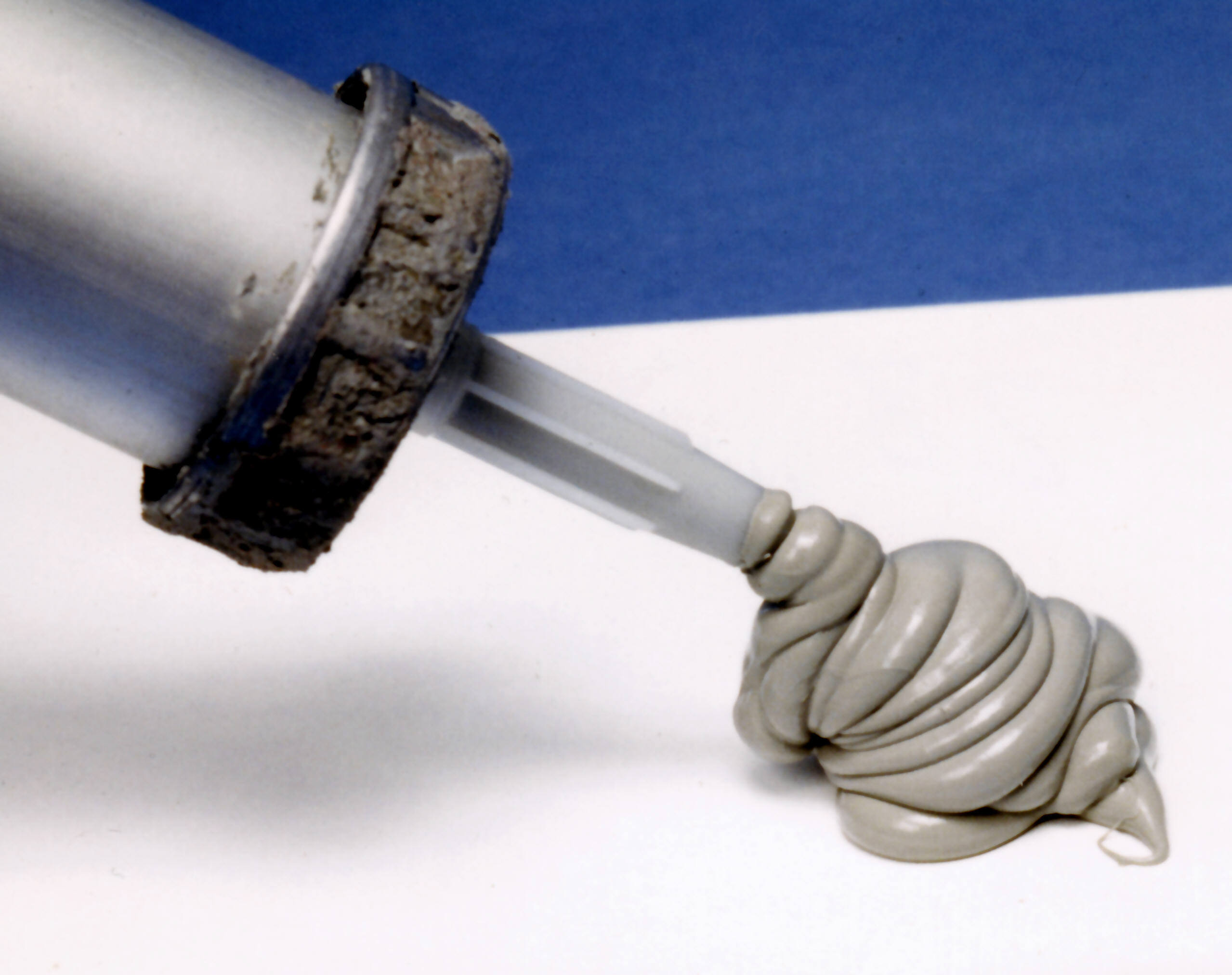

Silicone caulk from a tube, used in walls as a sealant & adhesive
Across nearly all wall types, the most common plastic components are:
- Insulation: Often made of expanded or extruded polystyrene, polyurethane, or fiberglass with plastic binders.
- Paint and finishes: Most modern interior and exterior paints are acrylic- or latex-based.
- Sealants and adhesives: Frequently formulated from synthetic polymers such as silicone, polyurethane, or epoxy.
Avoiding these materials can enable construction of a fully plastic-free wall assembly.
References
- Gypsum Wallboard Chemical Additives, Arpad Savoly and Dawn Elko, 2015.
- Drywall: Manufacture, Wikipedia, 2025.

